「テロメラーゼ」という単語をはじめて聞いた方も多いと思いますが、これは健康維持に欠かせない遺伝子のことで、今回の研究では、瞑想と生活習慣の改善が、テロメラーゼ生成に効果があることが判明しました。
本記事では、瞑想の効果の裏付けという視点で、この研究結果について詳しく見ていきます。
Contents
テロメラーゼ遺伝子とは
テロメアとは、クツ紐の先端で紐がほつれるのを防ぐ金具のようなものだ。染色体の先端にあるテロメアは、染色体がすり減るのを保護する働きをしている。つまり、細胞分裂の最中に、DNAが失われたり、損なわれないようにしているのだ。
それでも、細胞が分裂するたびに、いつの間にかテロメアの一部はすり減っていく。そして、テロメアが短くなりすぎると、染色体はそれ以上複製されなくなる。
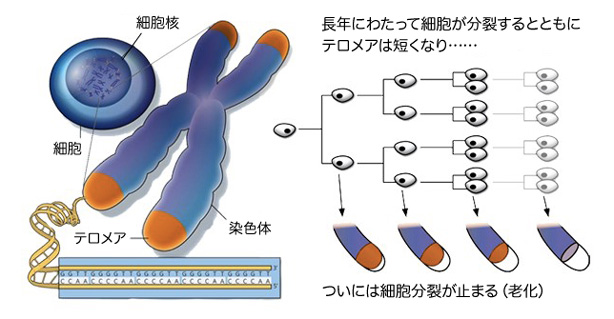
この染色体の先端を保護する金具(テロメア)を作り直しているのが、テロメラーゼと呼ばれる酵素だ。そのため、適切な健康を維持するためには、このテロメラーゼが適切に生成される必要があるといえる。
【研究結果】瞑想と生活習慣の改善が、テロメラーゼ生成に効果があることが判明

最近、超越瞑想と生活習慣の改善が、このテロメラーゼを生み出す2つの遺伝子を刺激することが、科学ジャーナル「PLOS ONE」に発表された新しい研究調査によって明らかになった。
研究によると、超越瞑想の実践と生活習慣を変えること、その両方が、テロメラーゼ(血圧、心血管疾患、死亡率の低下と関係している酵素)を生み出す遺伝子を活性化することが確認された。
心臓血管疾患や老化への効果が期待
超越瞑想(TM)に関する以前の研究は、TMによって高血圧、心臓発作、脳卒中、死亡率が減少し、生物学的老化がゆっくりになることを示している。
それに対して、今回の新しい研究では、DNAのレベルで起こっていることを調査した結果、超越瞑想によって、テロメラーゼ遺伝子の発現が増えることが明らかになり、それが心臓血管疾患や老化への効果に関係するのではないかと考えられている。
【研究方法】生活習慣改善を徹底する集団と超越瞑想(TM)を実施する集団で、テロメラーゼを比較

この予備研究の被験者となったのは、ハワード大学病院に通院している高血圧症の男女48名だ。
その半数の人は、超越瞑想を学び、基本的な健康教育のコースを受けるグループに割り当てられた。残りの半数の人は、体重を減らし、塩分を控え、定期的に運動をし、飲酒を控えるといった生活習慣の改善に専念するグループに割り当てられた。彼らは支援グループに支えられ、グループによる実習にも参加している。
16週間後に、両方のグループが、テロメラーゼ遺伝子の発現の増加と血圧の低下を示した。2つのグループの変化には、有意な差は見られなかった。その研究結果はまた、生活習慣を改善したグループは、彼らの日々の生活に関係した行動に、大きな変化を生み出したことを示していた。
この研究の共同執筆者であるハワード大学医学部のオテリオ・ランダル博士は、「アフリカ系アメリカ人を対象としたこの予備的研究は、ストレスの減少と生活習慣の改善は、テロメラーゼを増やし、血圧を下げることを示唆している」と結論付けた。
心臓の健康にとって励みとなる調査結果
今回の研究の共同執筆者ロバート・シュナイダー博士(FACC)は語る。
この研究は、米国国立衛生研究所(国立心臓・肺・血液研究所)とハワード大学医学部の臨床研究センターから資金提供を受けて行われた大規模な臨床試験の一部である。
ハワード大学医学部と、マハリシ経営大学の自然医学&防止センターおよび生理学部が共同でこの研究を行った。